前言
Nest.js 微服务实战系列计划实现一个简单的基于微服务的系统(TaoLJ),系统架构如下:
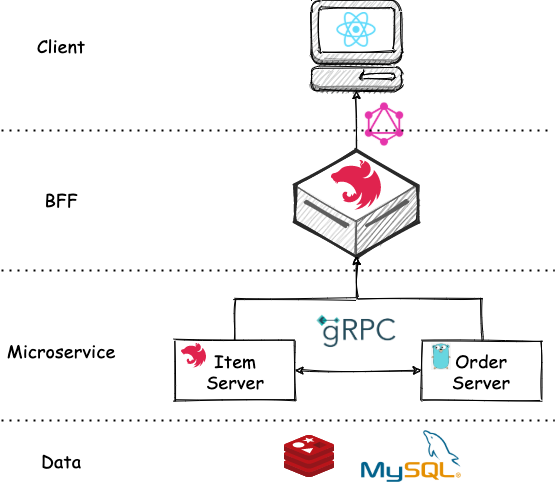
系统分为 Client,BFF(Backend For Frontend),Microservice,Data 四层。Client 使用 React 实现,与 BFF 通过 GraphQL 通信。BFF 使用 Nest.js 搭建,与 Microservice 之间通过 gRPC 通信。系统包含两个微服务 Item Server 和 Order Server,分别用 Node.js(Nest.js 框架) 和 Golang 来编写,微服务之间也通过 gRPC 通信。数据层就使用最常用的 MySQL 和 Redis。
本篇是 Nest.js 微服务实战的第一篇,搭建系统框架。
你也可以直接查看代码。
搭建 RPC 微服务
首先规划一下我们的目录结构:
1 | . |
由于 proto 文件需要被客户端和服务端共享,所以这里单独拿出来作为一个目录。接下来,先来搭建 Item Server。
Nest.js 搭建 Item Server 微服务
首先,我们在 proto 目录下新建 item.proto:
1 | syntax = "proto3"; |
然后,参考官网 gRPC 搭建出项目结构,如下所示:
1 | . |
其中 gen-code 用于存放通过 proto 文件生成的代码,那接下来就是生成代码。
需要先安装如下工具:
protoc:用来编译 proto 文件到代码的工具,本文使用 brew 安装,其他平台可自行搜索相关方式。ts-proto:protoc 的插件,用来生成 TS 代码
之后,在 item-server 目录下执行如下命令:
1 | protoc --plugin=./node_modules/.bin/protoc-gen-ts_proto --ts_proto_out=./src/gen-code --ts_proto_opt=nestJs=true --proto_path=../proto item.proto |
即可生成 Nest.js 风格的代码:
1 | . |
接着,我们需要按照 proto 文件中的定义实现我们的 controller:
1 | import {Controller} from '@nestjs/common' |
这样,Item Server RPC 服务算是搭建好了,我们写一个客户端来测试一下:
1 | const path = require('path') |
验证无误,继续搭建 Order Server RPC 服务。
Golang 搭建 Order Server 微服务
本文 Golang 版本为 1.19
首先同样在 proto 目录下新建 order.proto,这里就不贴代码了。
然后,在 order-server 目录下执行:
1 | protoc --go_out=./pb --go_opt=paths=source_relative --proto_path={Your path here}/proto \ |
则会生成 Golang 所需的代码:
1 | . |
然后,编写我们的服务端代码:
1 | package main |
这样,我们的 Golang RPC 服务端就搭好了。客户端则同上文类似,换一下 proto 文件和端口号即可。
搭建 BFF 服务
为了更好的理解 GraphQL,我们先用纯 Node.js 搭建一遍,然后再使用 Nest.js 实现一遍。
Node.js 版
一个简单的基于 express 的 GraphQL 服务如下:
1 | const express = require('express') |
显然,这里最重要的是 schema.js 这个文件:
1 | const Item = new GraphQLObjectType({ |
该文件中定义了实体模型 Item 以及我们的 RootQueries。这里的 RootQueries 可以看成我们的接口定义,但其实它也只是一个 Object Type 而已,她每一个 Field 都实现了一个 resolve,该函数的返回值就是这个字段的值。
启动客户端,在浏览器中打开 http://localhost:4000/graphql 就可以体验了:
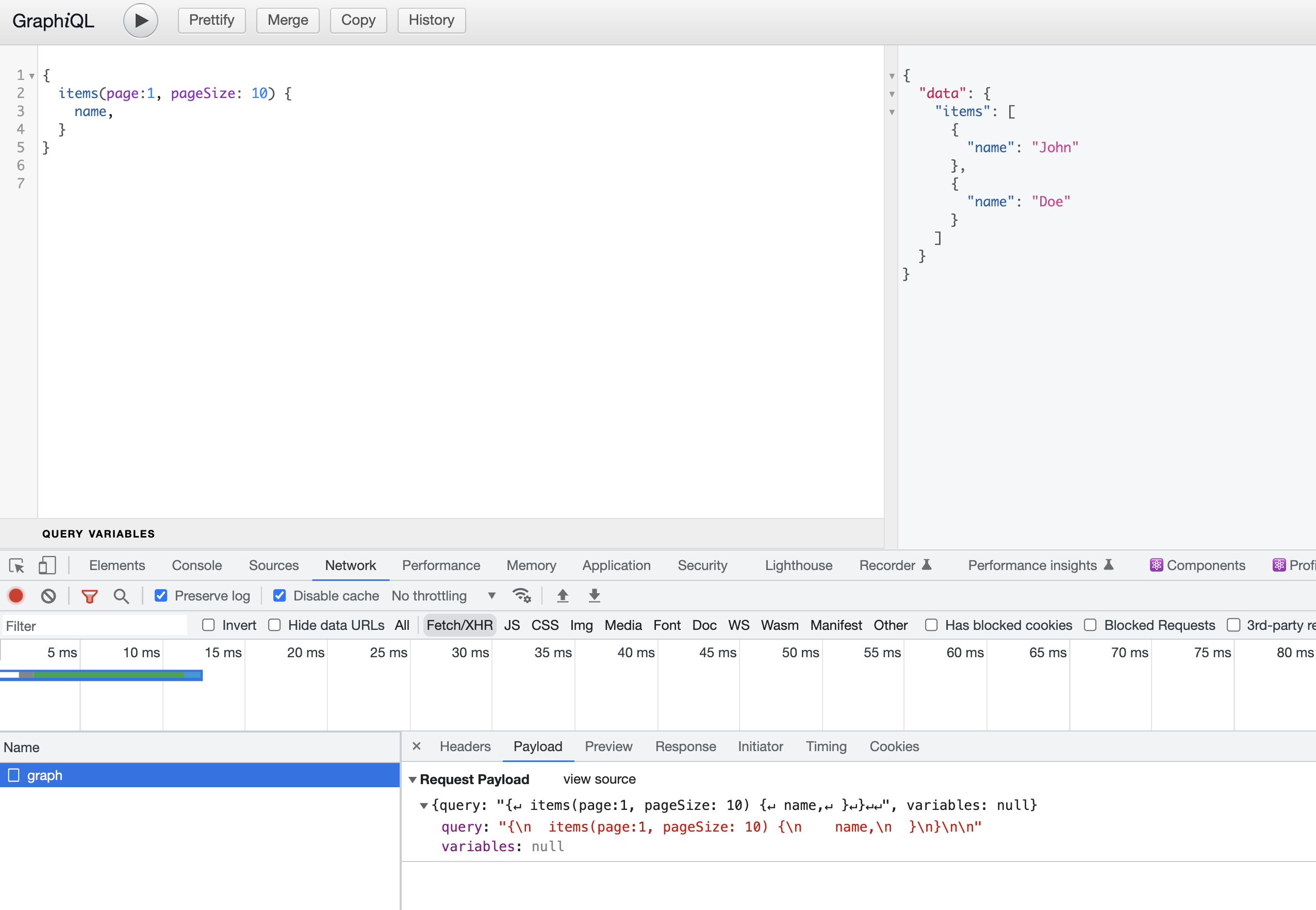
GraphQL 的一大魅力在于客户端可以自由定义返回的字段,我们用另一个例子更好的体会一下:
1 | const RootQueries = new GraphQLObjectType({ |
上面的例子用来查询一个 Order,当客户端没有指定返回 items 字段时,只调用 Order Server 的接口即可。否则需要调用 Item Server 的接口。
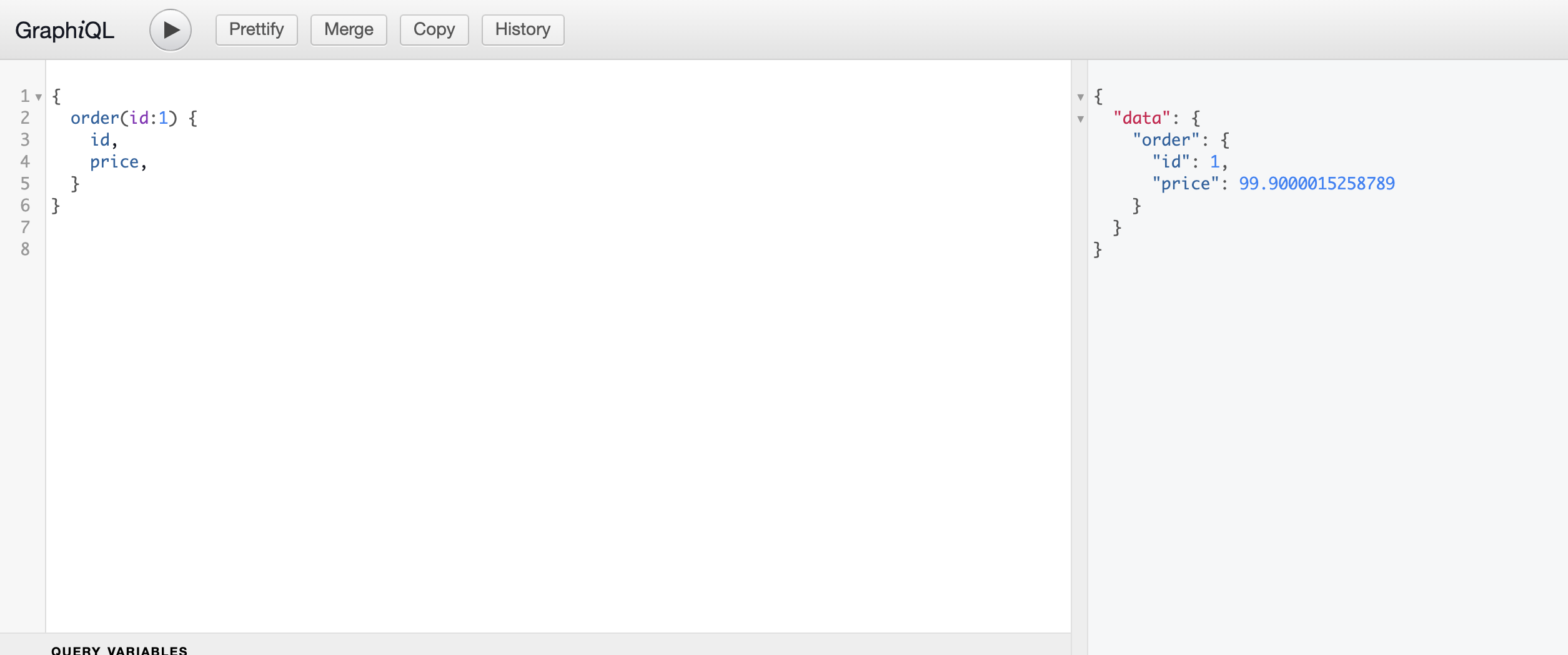
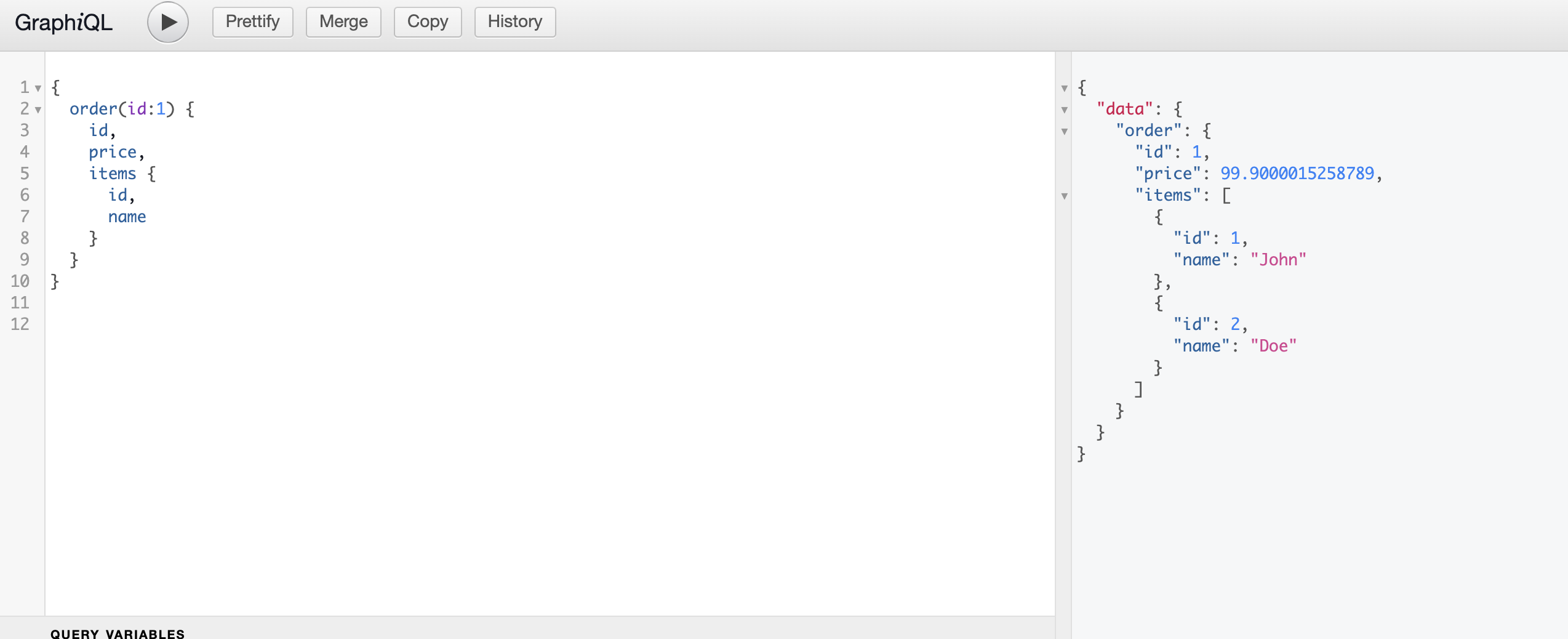
接下来看看使用 Nest.js 如何实现相同的功能。
Nest.js 版
Nest.js 官网 中搭建 GraphQL 服务有 Code First 和 Schema First 两种方式,我们这里选择 Code First 方式,即自己定义 TS 的对象模型,然后自动生成 schema。
首先,我们定义 Item 和 Order 两个模型:
1 | import {Field, ID, ObjectType, Float, Int} from '@nestjs/graphql' |
然后编写业务逻辑相关的部分,这里以 Item 这个模块为例,每个模块包含 module, resolver, service 三个文件:
1 | . |
其中 item.resolver.ts 和 item.service.ts 如下:
1 | // item.resolver.ts |
其中的 rpcService 来自 rpc 这个模块,这里会初始化对接 item-server 和 order-server 的 RPC 客户端 itemServiceClient 和 orderServiceClient,代码就不贴了,直接看 Github 吧。
GraphQL 只是一个协议,最后还是需要一个网络服务来驱动,Nest.js 官网提供了 @nestjs/apollo 和 @nestjs/mercurius 两种,我们这里选择使用 express-graphql 来自定义:
1 | class ExpressGraphQLDriver extends AbstractGraphQLDriver { |
一切就绪后打开 http://localhost:9000/graphql 即可跟上面一样进行调试。
Client
最后,让我们来基于 React 写个简单的客户端,其中 GraphQL 客户端使用 @appollo/client 这个库,需要在入口进行配置:
1 | import {ApolloClient, InMemoryCache, ApolloProvider, gql} from '@apollo/client' |
组件中,按照如下方式使用即可:
1 |
|
所有服务都启动好以后,打开我们的客户端,就可以看到我们系统的雏形了:
终于赶在过年前把系统雏形打好了,接下来的计划是什么呢?当然是过年了!